On this page we will provide you with the answer to the question “ What is Kanban ”, by providing you with both a definition and simple explanation of it.
Kanban is another of the Japanese words that have become a part of the Lean vocabulary. The base definition of the word Kanban in Japanese is signboard or billboard, it is from this basic meaning that its Lean definition grew from. But like many words it has multiple meanings depending on it use.
Lean Definitions for Kanban:
- A small signboard that is the key control for Just in Time Production
- Instruction card for production or conveyance
- A visual control tool
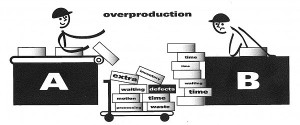
- To prevent over-production
- To detect irregular processes
- A tool for kaizen
[wpdm_tree category=”kanban-card-templates”]
Kanban Explanation
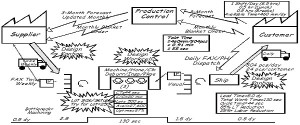
Kanban is a card or sign system (we will use the words Kanban card from now on) used to control production and movement of materials through a set of processes, in an orderly and timely fashion. It has the added benefits of limiting inventory, and identifying process problems.
Kanban card are a control system in that the presence of a card signals the next action for a process. The card tells the operator of the process what the next job they will do is. It also limits the production to a specified number of units that are indicated on the card, or by the container the card is attached to. After a process is completed the card will identify were the processed materials are to go to next. This is how Kanban maintains orderly production.
Kanban enforces timely production, in that the number of Kanban cards is related to the Takt Time for the product being produced. A build up or lack of Kanban cards at any point visually reveals a problem at that point in the operation.
The use of Kanban supports Kaizen, as it reveals problems that need to be dealt with in a manner that is visually seen by all employees.
So What is Kanban?
Kanban is a card system used to control and visually monitor processes in any operation, that identifies problems and prevents over-production.
Kanban cards come in many types, some of which are, withdrawal Kanban, in process Kanban, supplier Kanban, production instruction Kanban, signal Kanban, and temporary Kanban to name some common ones. They also come in many shapes and sizes, and can contain very little information such as a part identifier, or they can contain the instructions for every process the material will move through, this depends on the needs of the user. They can also just move about a single process or they can travel through the whole value stream, which will also depend upon the user’s needs.
[wpdm_category id=”kanban-card-templates” operator=”IN” title=”1″ desc=”1″ toolbar=”1″ order_by=”field name” order=”asc or desc” item_per_page=”20″ template=”temaplte name or ID” cols=2 colspad=2 colsphone=1]